Basic Linux Commands for beginners with example
1.Usage of Basic Linux Commands, File Utilities Commands.
| Command | Description |
| pwd | Present working directory |
| ls | Lists all files and directories in the present working directory |
| ls – R | Lists files in sub-directories |
| ls – a | Lists hidden files |
| ls – al | Lists files and directories with detailed information like permissions, size, owner, etc. |
| clear | Clears the terminal |
| whoami | Display User ID |
| uname | Display Operation System |
| tail <file name> | The tail command is similar to the head command. The difference between both commands is that it displays the last ten lines of the file content |
| find . -name “*.pdf” | The find command is used to find a particular file within a directory. |
| cat > filename | Creates a new file |
| cat filename | Displays the file content |
| cat file1 file2 > file3 | Joins two files (file1, file2) and stores the output in a new file (file3) |
| tac <file name> | The tac command is the reverse of cat command, as its name specified. It displays the file content in reverse order (from the last line). |
| touch <file1> <file2> | Change the file access and modification time if file does not exist will create with default permission. |
| locate <file name> | The locate command is used to search a file by file name. |
| sort <file name> | The sort command is used to sort files in alphabetical order. |
| command | grep <searchWord> cat marks.txt | grep 9 | The grep is the most powerful and used filter in a Linux system. The ‘grep’ stands for “global regular expression print.” It is useful for searching the content from a file. Generally, it is used with the pipe. |
| less <file name> | The less command is similar to the more command |
| mv <file name> <directory path> | Moves the files to the new location |
| mv filename new_file_name | Renames the file to a new filename |
| rm rfilename | Deletes a file |
| man | Gives help information on a command |
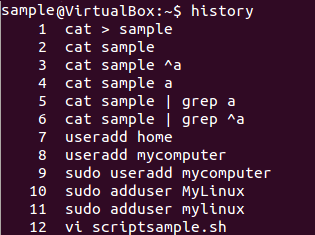
| history | Gives a list of all past basic Linux commands list typed in the current terminal session |
| cp <existing file name> <new file name> | Copy file |
| mkdir directoryname | Creates a new directory in the present working directory or a at the specified path |
| cd | Change directory |
| cd .. | Back one step current directory |
| rmdir | Deletes a directory |
| mv | Rename a directory |
| command | tr <‘old’> <‘new’> cat marks.txt | tr ‘prcu’ ‘PRCU’ | The tr command is used to translate the file content like from lower case to upper case. |
| date | The date command is used to display date, time, time zone, and more. |
| time | The time command is used to display the time to execute a command. |
| cal | The cal command is used to display the current month’s calendar with the current date highlighted. |
| pr -x | Divides the file into x columns |
| pr -h | Assigns a header to the file |
| pr -n | Denotes the file with Line Numbers |
| head <file name> head demo.txt | The head command is used to display the content of a file. It displays the first 10 lines of a file. |
| tail <file name> tail demo.txt | The tail command is similar to the head command. The difference between both commands is that it displays the last ten lines of the file content. |
| wc <file name> | The wc command is used to count the lines, words, and characters in a file. |
| sudo | Allows regular users to run programs with the security privileges of the super user or root |
| sudo useradd username | Create New User |
| sudo -s | switch root user |
| sudo passwd username | Change user password |
| sudo apt-get update | Command used to install and update packages |
Listing files (ls)
Linux system, use the ‘ls ‘ command. It shows the files /directories in your current directory.

Note:
• Directories are show in blue color.
• Files are show in white.
• You will find similar color schemes in different flavors of Linux/Unix.
Your “Music” folder has following sub-directories and files.
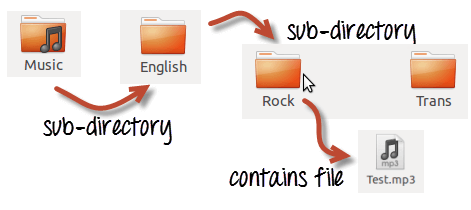
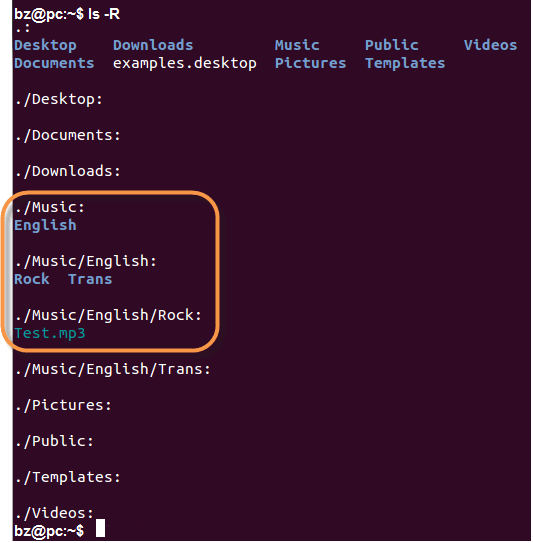
‘ls -R ‘ to shows all the files not only in directories but also subdirectories
Note: These Linux basics commands are case-sensitive. If you enter, “ls – r ” you will get an error.
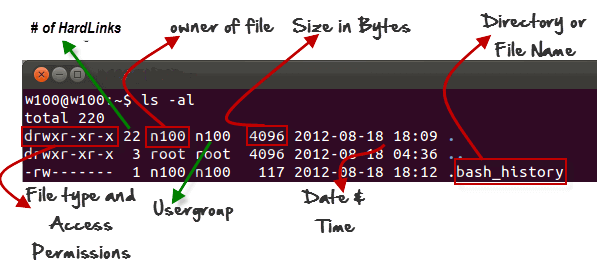
‘ls -al ‘ The command provides information in a columns format. The columns contain the following information:
Example –
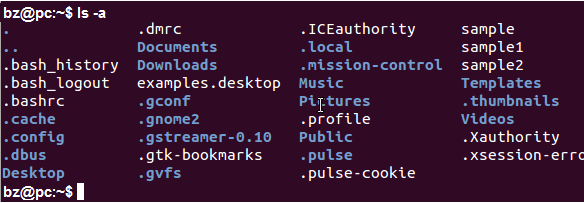
Listing Hidden Files
ls -a
Creating & Viewing Files
The ‘cat’ command is used to display text files. It can also combining and creating new text files. Let’s see how it works.
To create a new file, use the command
1. cat > filename
2. Press ‘ctrl + d ‘ Save File.
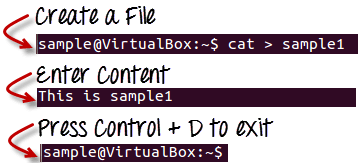
To view a file, use the command –
cat filename
Let’s see the file we just created –

Let’s see another file sample2

The syntax to combine 2 files is –
cat file1 file2 > newfilename
Let’s combine sample 1 and sample 2.
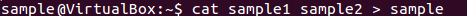
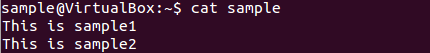
To view the new combo file “sample ” use the command
cat sample
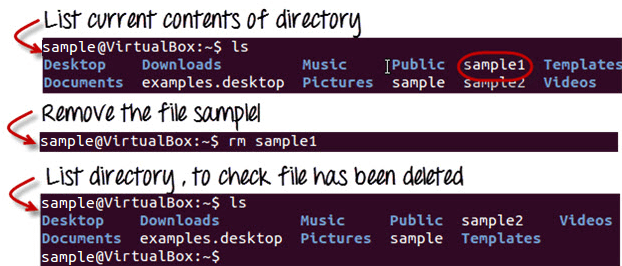
Deleting Files
rm filename
Moving and Re-naming files
To move a file, use the command.
mv filename new_file_location
Suppose we want to move the file “sample2” to location /home/cse/Documents. Executing the command
mv sample2 /home/cse/Documents
bz@pc:~$ sudo mv sample2 /home/cse/Documents
[sudo] password for bz: ****
bz@pc:~$
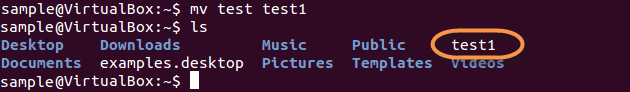
For renaming file:
mv filename newfilename
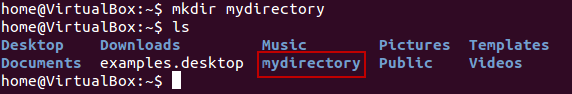
Directories can be created on a Linux operating system using the following command
mkdir directoryname
Example:-
mkdir mydirectory
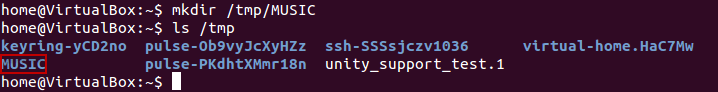
Will create a directory ‘Music’ under ‘/tmp’ directory
mkdir /tmp/MUSIC
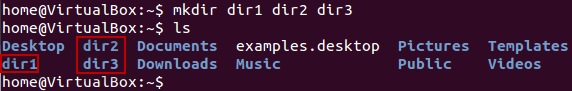
You can also create more than one directory at a time.
Removing Directories
rmdir mydirectory
will delete the directory mydirectory
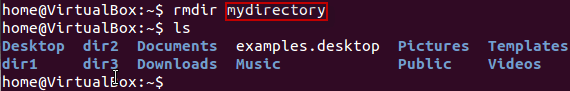
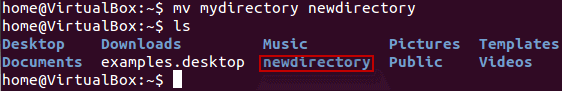
Renaming Directory
mv directoryname newdirectoryname
The History Command
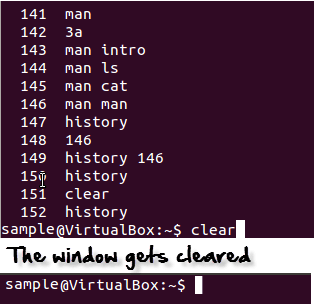
The clear command
This command clears all screen.
Assigning a header
pr -h “Header” Filename
The ‘-h’ options assigns “header” value as the report header.
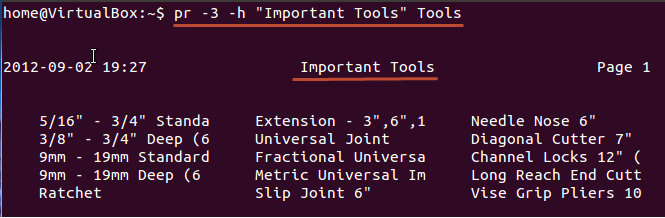
As shown above, we have arranged the file in 3 columns and assigned a header
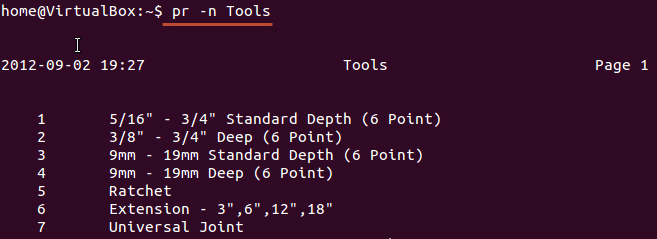
Display all lines with numbers
Example:
pr -n Filename
This command display all the lines in the file with numbers.
Vi Editor Commands and Networking Commands in Linux
